All You Need To Know About Dairy Milk Quality 2023 Addition

Host
Global Dairy Production
Target Audience
Beef And Dairy Farmers
Introduction
Milk is a natural product containing almost all the essential nutrients dissolved or in finely dispersed state. Has very high digestibility of nutritional components – up to 95-98%. Protein is presented by casein, albumin and globulin.
Milk Characteristics
- Up to 3.7% Triglycerides – presented in the emulsion form, improves absorption of Vit A and D in dairy products.
- Melting point of Triglycerides is below human body temp.
- The main carbohydrate is lactose (glucose and galactose). Lactose provides milk sweet flavor.
- Nearly 30 Vitamins including fat-soluble (A, D), and water-soluble (riboflavin, pantothenic acid, pyridoxine, ascorbic acid).
- Calcium is the most prominent mineral.
Quality milk
- milk that meets accepted standards for CHEMICAL COMPOSITION, PURITY and LEVELS OF DIFFERENT MICRO-ORGANISMS
- Contains 87% water, therefore, prone to adulteration
- Milk is high in nutritive value – ideal medium for the rapid multiplication of bacteria
Why Quality Milk?
- Unhygienic production = loss of income
- Storage at ambient temps accelerates spoilage
- Quality raw milk makes Quality products
- Milk quality assessment is done to make sure that MILK PRODUCTS, PROCESSORS and MARKETING AGENCIES adhere to accepted codes of practices
3 Reasons for quality control
Milk producer: expects a fair price in accordance with the quality of milk she/he produces.
Milk processor: pays the producer expecting a quality product because the milk should be suitable for processing into various dairy products.
Consumer : expects to pay a fair price for milk and milk products
Quality control during production, transport & reception
At farm: use approved practices for production (cleanliness and drugs) and handling (adulteration and handling conditions)
Milk collection Centres: Check for wholesomeness, bacteriological, and chemical quality
At dairy factories: Check quality on milk from individual farmers or bulked milk from various collecting centres
Public & government agencies: ensure that health and nutritional status of the people is protected and prices paid are fair to milk producers, processors and consumers
Quality control during processing and marketing
Within dairy factory:
– ensure hygiene handling,
– carry out quality assurance tests (e.g. phosphatase test used on pasteurized milk and the acidity development test done on U.H.T milk.
During marketing of processed products:
– Public health authorities impounds sub – standard or contaminated foodstuffs
– can prosecute culprits
Milk quality parameters – introduction
By law, only fresh, palatable and healthy milk should be marketed
Milk comprises of water (87%) and Total Solids (TS) – 13% (i.e. Fats (Butter fat) and SOLIDS-NOT-FAT (SNF)
Main components are FAT, PROTEIN, LACTOSE, VITAMINS and MINERALS
ALSO READ: Approved Principles of Dairy Cow Nutrition
Milk quality parameters – composition
Compositional quality of milk can be expressed in two ways – choice depends on demands by processor:
i) Butterfat (BF), Solids Not Fat (SNF) and Total Solids (TS)
ii) Butterfat (BF), Protein, Lactose and Total Solids (TS)
Minimum legal standard for BF = 3%
Minimum Legal Standard SNF = 8%
Minimum Legal Standard TS = 12%
Milk quality parameters – hygiene standards
Hygiene standards are based on number of spoilage bacteria present in raw milk at dairy farm
Can use direct counting of spoilage bacteria or use chemical tests that indicate presence
Total bacterial count – Viable count assays (Colony counting) method
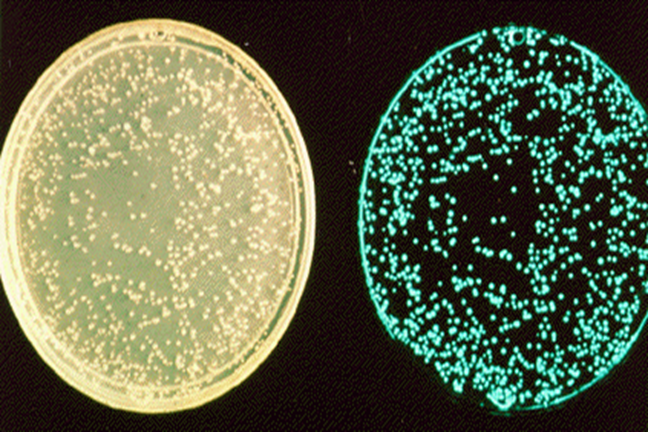
Colony counting is done after plating dilutions of the sample onto growth medium.
Assumption: each viable cell gives rise to a colony.
Two methods can be used:
1- Spread plates: A diluted sample is spread onto the surface of an agar plate
2- Pour plates: Microorganisms are mixed with molten agar and poured into a petri dish.
Pour plate method to count bacteria
Advantages:
-The method can be made to be very sensitive.
-One count can be subsets of the population.
Disadvantages:
-Colony-forming units may underestimate cell numbers because of clumping or chains of cells.
-Counts require at least a few hours, usually overnight, for incubation.
Payment or penalty is based on national weighted average composition for the previous year
Total bacterial count – Coulter Counter
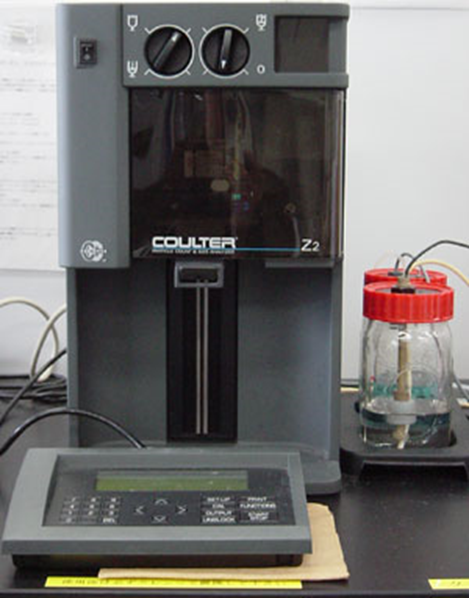

Electronic counting
Detects the difference in current as individual microorganisms pass through a small orifice
Very fast, easy but very expensive (USD 13 500)
Reasons for serial dilutions
Serial dilutions allow one to dilute a sample of bacteria to the point that the total number of bacteria can be counted on an agar plate.
Bacteria occur in large numbers because they undergo exponential growth.
In order to count the number of bacteria, each colony must be single and distinct.
Number of countable colonies per plate is 30-300
ALSO READ: Starting Your Own Dairy Enterprises And Becoming A Dairy Farmer In South Africa
Methylene Blue test
Was the most commonly used to test for milk hygiene standards
Was replaced by TBC method to match world standard tests and requirements
A premium was paid if decolouration of methylene blue exceeded 3hr in October to March or 4 hrs (April to September) and a penalty for every ½ hr below those standards
Procedure – Methylene blue test
Transfer 10 ml of each milk sample into appropriately labeled test tube.
Add 1 ml of redox indicator, methylene blue to each test tube containing milk sample.
Tighten the test tube mouth with stoppers. Gently invert the tubes at about four or five times to ensure proper mixing of the methylene blue solution.
Keep the tubes in the water bath at 37 o C
Note the incubation time. That is, the time elapsed for the color to turn whitish appearance.
Stabilize the tubes for 5 minutes.
Conclusively, Milk quality should be able to meet accepted standards and requires maximum levels of hygiene. Fresh milk has a pH of 6.7 (i.e. slightly acidic). Acidity test was used at DDP collection depos to test milk quality. It is an indication of lactose fermentation.
ALSO CHECK: 4 Ways To Increase Live Weight In broilers And Egg Size In layers
For more updates On Agric Tech Opportunities kindly join the social groups below:




